IGIPT: Integrated Genomic Island Prediction Tool
The genomic DNA of different organisms has a particular mean G+C content. The bias in codon usage is species specific i.e. the genes in a given genome use the same coding strategy for choices among synonymous codons. Parameters such as G+C content, Genome Signature, Codon Usage and Amino Acid Bias values have been used to determine the acquisition of genomic portions by HGT.
-
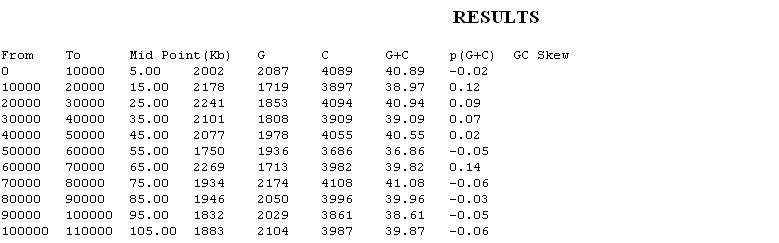
GC content anomalies: The G+C frequency is evaluated by taking a sliding window W that may be of different lengths, singling out windows significantly deviant in GC content. The G+C content of the alien genomic strips may be higher or lower than the mean G+C content of their own genome.
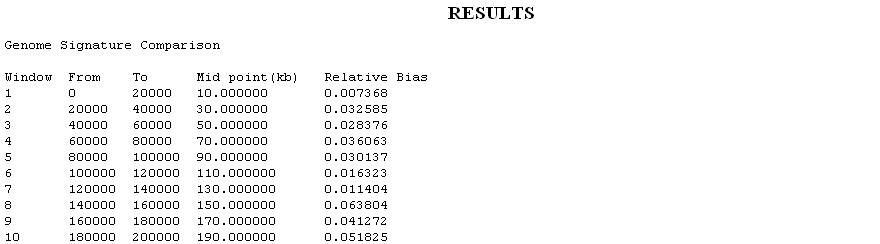
- Genomic Signature contrasts (Dinucleotide bias): A Genome has characteristic values of the dinucleotides. Any deviation from the average values of the dinucleotide indicates a horizontal transfer event. Such a measure displaying contrasts in dinucleotide frequencies is known as Genome Signature. The GS Profile consists of the array of dinucleotide relative abundance values.The dinucleotide biases assess differences between the observed dinucleotide frequencies and those expected from random associations of the component mononucleotide frequencies.The genome Signature is calculated by the Formula:
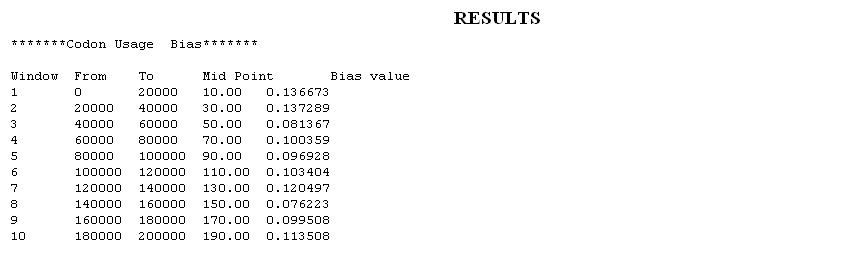
- Extremes of Codon bias: Each genome has a characteristic value of Codn Bias, which refers to the unequal use of synonymous codons for encoding amino acids. Hence any deviation in the values of usage of synonymous codons indicates a probable genomic island. For the calculation of the codon Bias the average codon frequencies for codons coding for a particular amino acid are normalized. The codon usage difference of the gene family F relative to the gene family G, termed the codon bias of F with respect to G is calculated.
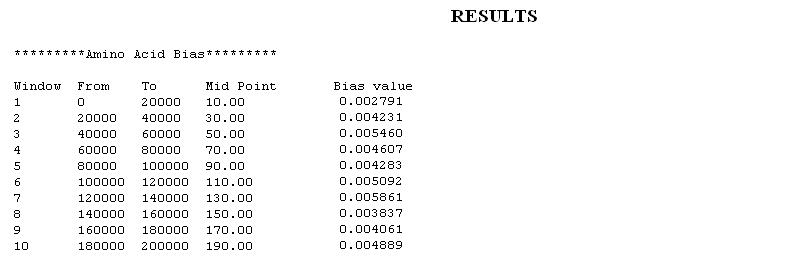
- Amino Acid Bias: Similar to Codon Bias the Amino Acid Usage is also characteristic of a species. The amino acid frequencies of the gene set Fw is compared with the average amino acid frequencies of the genome. Windows containing genes with significant deviations in overall amino acid usages might signify a Genomic Island.
- GC Content at different Codon Positions:For this measure, the total G+C content ([G+C]T) and G+C contents at the first and third codon positions ([G+C]1 and [G+C]3) of every ORF are computed. The compositional bias at the first and third positions is reported to be positively correlated to expressivity and genomic G+C content. Extraneous origin of the gene in terms of G+C content is considered if its [G+C]T deviates over 1.5 Standard Deviations or if deviations of [G+C]1 and [G+C]3 are of the same sign and at least one of them is over 1.5 Standard deviations.
Parameters
- Window Size :The analysis is done over a sliding window across the genome. Hence this parameter describes the size of the Window (W). The size may range from 5000, 10000, 20000. The default value for the parameter is 10000.
- Standard Deviation :The results indicate a large number of probable genomic islands. In order to screen a set of islands which are statistically significant above the average value of the particular measure this parameter is used. Eg: 1.5 or 2. Standard Deviations above the mean. The default value for the parameter is1.5.
Sample Input Formats:
The input file is the Whole Genome File of the Prokaryotic Organism in case of xcalculation of the GC Content and Genome Signature and the Complete Gene File in case of Codon Bias and Amino Acid Bias.
- Whole Gene Sequence

- Whole Genome Sequence

Outputs